If you’re planning to launch a crypto business in Dubai and you’re leaning toward DMCC, you will have to figure out whether your business model is non-regulated, NOC-based, or fully regulated under VARA.
A DMCC trade licence proves your company exists, while VARA determines whether you can conduct regulated virtual-asset activity. The path you take depends on what your product actually does and who you target.
This guide helps you in mapping your activity, choosing the correct track, and efficiently launching a crypto company in DMCC in 2026.
TL;DR
DMCC is a leading Dubai free zone for Web3; a trade licence creates the company but is not permission to conduct regulated crypto activity.
Three paths: (1) Non-regulated (no VARA approval), (2) Non-regulated with VARA NOC (e.g., VA proprietary trading), (3) Regulated VASP with full VARA licence (exchange, brokerage, custody).
Process: define activities → DMCC pre-approval → company registration → VARA IDQ & ATI (if applicable) → final VARA authorisation → full DMCC licence.
Timelines: 2-3 weeks (non-regulated), 4-8 weeks (VARA NOC), ~7-9+ months end-to-end for VASP.
Costs: DMCC company set-up + office + visas ≈ USD 14k-18k baseline, plus VARA application/supervision fees for regulated models.
NeosLegal supports crypto founders end-to-end, from structuring and licensing strategy to incorporation, banking, and ongoing regulatory advisory, having structured over 300 crypto and Web3 projects in the UAE and internationally since 2016.
Key Definitions:
1. What Is a VARA VASP Licence?
A Virtual Asset Service Provider (VASP) licence is a regulatory authorisation issued by Dubai’s Virtual Assets Regulatory Authority (VARA) allowing a company to conduct regulated virtual asset activities such as exchanges, broker-dealer services, custody, or client asset handling. It is required whenever an activity falls within VARA’s regulatory perimeter.
2. What Is a VARA Non-Objection Certificate (NOC)?
A VARA Non-Objection Certificate (NOC) is a formal written confirmation from VARA stating that a specific non-regulated crypto activity may be carried out without a full VASP licence. While the activity is not regulated, the NOC confirms VARA’s acknowledgment and is mandatory before operations commence.
3. What Is an IDQ (Initial Disclosure Questionnaire)?
The Initial Disclosure Questionnaire (IDQ) is a regulatory submission to VARA outlining a company’s business model, governance, risk controls, and compliance framework. It forms the basis for VARA’s Approval to Incorporate and sets the foundation for the company’s ongoing regulatory obligations. Early legal review of VARA IDQ reduces licensing timelines materially.
Table of Contents:
- Why DMCC Is a Leading Hub for Crypto & Web3 Companies.
- Step 1- Defining Your Crypto Business Activities in DMCC.
- Step 2 – DMCC Pre-Approval and Company Registration.
- Step 3 – VARA Licensing, Office Setup & Operational Compliance.
- How Long Does DMCC Crypto Licensing Take?
- How Much Does It Cost to Set Up a Crypto Company in DMCC?
- Top 3 Mistakes Crypto Founders Make When Setting Up in DMCC.
- FAQs
Over the past few years, it’s become undeniable that Dubai has emerged as the global hub for the Web3 and crypto industry. Its rise has been both rapid and deliberate. Unlike many other jurisdictions, Dubai adopted an innovation-first mindset which was evident in its groundbreaking move to establish the world’s first dedicated crypto regulator.
With that, and a series of complementary initiatives including clear licensing frameworks, public-private partnerships, and ecosystem-level incentives, it’s no surprise that Dubai, and the broader UAE, is now seen as the undisputed epicentre of the global crypto economy.
Within Dubai, DMCC (Dubai Multi Commodities Centre) stands out as a leading free zone for Web3 and crypto businesses. Through the DMCC Crypto Centre, it has developed a structured environment supporting companies across the entire blockchain and virtual assets value chain.
Why DMCC Is a Leading Hub for Crypto & Web3 Companies
The DMCC Crypto Centre is a purpose-built Web3 hub offering access to crypto-related business activities, acceleration programmes, technology infrastructure, media exposure, investor networks, and global talent.
Located at the heart of Dubai’s blockchain ecosystem, DMCC provides companies with the legal and operational foundations required to launch and scale crypto businesses in a regulated yet commercially practical environment.
For entrepreneurs and companies looking to establish a serious presence in the Web3 space, DMCC offers one of the most streamlined and supportive environments to launch and grow a crypto business.
DMCC is particularly suitable for founders and companies seeking:
- A recognised UAE jurisdiction for crypto operations.
- Access to Dubai’s Web3 ecosystem and capital markets.
- A clear licensing pathway aligned with VARA where applicable.
- Scalable infrastructure for long-term growth.
- A recognised UAE jurisdiction for crypto operations.
Step 1- Defining Your Crypto Business Activities in DMCC
Setting up a crypto business in Dubai involves a clear and structured process and it begins with defining the company’s main business activities.
There are three categories of crypto-related activities available, issued depending on your company’s line of business.
These activities can be divided into:
1. Non-Regulated Activities (No VARA Approval Required)
These activities fall outside the regulatory scope of the Virtual Assets Regulatory Authority (VARA), allowing companies to operate without obtaining any prior approval or certification from VARA. Examples include software or technology development, consulting services, marketing, etc. In this scenario, a DMCC business licence is sufficient to operate. In these cases only a trade license is required to operate.
2. Non-Regulated Activities Requiring a VARA Non-Objection Certificate (NOC)
Certain non-regulated activities, such as virtual asset proprietary trading (VA proprietary trading), are not directly regulated but require formal acknowledgement and issuance of an NOC from VARA prior to commencing operations. In this scenario, the company will require a DMCC licence and a VARA NOC
3. Regulated Virtual Asset Activities (VARA VASP Licence Required)
VARA regulations directly govern these activities. Companies engaging in exchange services, broker-dealer services, and other regulated activities must obtain a Virtual Asset Service Provider (VASP) licence from VARA and comply fully with its regulatory requirements. In this scenario, the company will require a DMCC business licence and a VARA regulatory licence.
When Do You Need VARA Approval in DMCC?
A DMCC business licence confirms legal existence, but it is not a regulatory licence.
VARA approval is required based on the activity conducted, not merely the jurisdiction in which the company is incorporated.
From a legal standpoint, it’s critical to define your business model with precision. Misalignment between your commercial intent and licensed activity may delay approvals, attract regulatory enforcement as well as fines and personal liability for founders and managers.
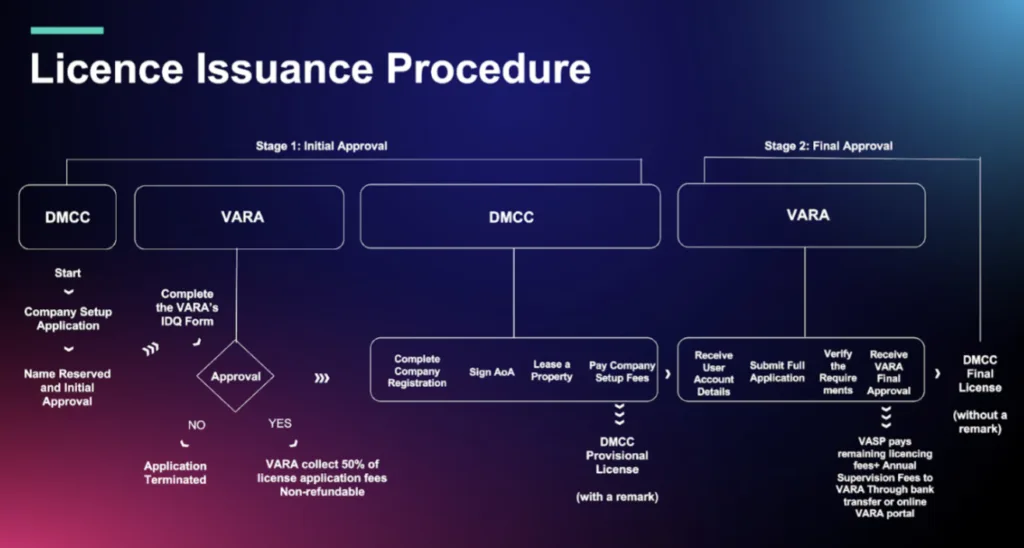
Step 2 - DMCC Pre-Approval and Company Registration
The registration and pre-approval process depends on the business activity. Once the business activity is selected, the process is the following:
- Non-regulated business activities that do not require any regulatory approval:
-
-
- The applicant completes a basic DMCC questionnaire confirming the business and revenue model.
- DMCC provides pre-approval and grants access to the DMCC portal to start the company set-up process.
- The applicant completes the company set-up process by providing the required information and documents, completing the identity verification and then digitally signing the shareholder resolution and Articles of Association.
-
2. Non-regulated business activities that require a Non-Objection Certificate (NOC) from VARA:
-
-
- The applicant completes a basic DMCC questionnaire confirming the business and revenue model.
- DMCC provides pre-approval and grants access to the DMCC portal to start the company set-up process.
- The applicant submits the VARA IDQ (Initial Disclosure Questionnaire) to obtain the required NOC.
- The applicant completes the company set-up process by providing the required information and documents, completing the identity verification and then digitally signing the shareholder resolution and Articles of Association.
-
3. Regulated VASP activities:
-
-
- The applicant carries out a regulatory assessment to understand the DMCC regulations and VARA requirements and determine the most suitable licence activity.
- DMCC grants access to the DMCC portal to start the Initial Stage of the company set-up process up to the company Name Reservation.
- The applicant completes and submits the VARA Initial Disclosure Questionnaire (IDQ), which will be provided upon finalising the previous step.
- Approval to Incorporate (ATI): VARA grants initial approval based on the information submitted in the IDQ, and the Company is to pay 50% of the VARA licensing fees (the fee structure can be found here: Schedule 2 – Supervision and Authorisation Fees ).
- Company Registration: The applicant completes the company set-up process by providing the required information and documents, completing the identity verification and then digitally signing the shareholder resolution and Articles of Association.
-
Applicants are strongly encouraged to engage with specialist UAE crypto lawyer early to preempt any issues in the VARA Initial Disclosure Questionnaire, which forms the basis for both your Approval to Incorporate and future regulatory obligations.
At this stage, the Company has its legal entity structure and initial approval from the regulator. DMCC then issues a provisional license.
Step 3 - VARA Licensing, Office Setup & Operational Compliance
After obtaining DMCC’s provisional license, which typically takes 1 to 2 months and marks the completion of Stage 1, companies proceed to Stage 2 to finalise regulatory requirements with VARA:
- Regulatory Process: The company starts the regulatory process with VARA by submitting all necessary documents.
- Final Licence Fees: The company pays the remaining 50% of the VARA application fee and the VARA annual supervision fee.
- Final Approval: VARA grants the Company final approval, and DMCC issues the full licence.
This marks the completion of Stage 2, which is expected to take around 6+ months and results in the issuance of the final DMCC licence with no remarks.
Also, companies must finalise operational requirements to begin activities in DMCC:
- Office Space
Secure physical office space within DMCC jurisdiction, choosing between flexible solutions like co-working desks for small teams or fully serviced offices for larger businesses. A finalised lease agreement is mandatory before licence issuance. - Employment and Visas
Facilitate visas for employees, investors, and family members, ensuring compliance with UAE labour laws, employee registration under DMCC, and completion of medical tests and Emirates ID procedures. - Bank Account Setup
Open a corporate bank account in the UAE, which involves submitting business plans, licencing documents, and AML/KYC policies. Expect thorough due diligence from banking institutions due to the nature of crypto activities. - Regulatory and AML/KYC Compliance
Implement robust AML/KYC frameworks, appoint a dedicated Compliance Officer, and ensure meticulous record-keeping to comply with UAE regulatory standards.
These combined processes form the foundational steps required to legally establish and operate your crypto business in DMCC.
Step Up Requirements Snapshot:
- Online pre-approval application form.
- Passport copy (a copy of the UAE residency visa and Emirates ID if applicable).
- Proof of residential address in the country of residence (for example, a utility bill).
- If setting up a branch or a subsidiary, copies of the parent company documents.
How Long Does DMCC Crypto Licensing Take?
The timeline for setting up a crypto company in DMCC depends primarily on the type of crypto activity and whether VARA regulatory approval is required. While non-regulated activities can be launched relatively quickly, regulated virtual asset activities involve a multi-stage regulatory process and significantly longer timelines.
Non-Regulated Crypto Activities (No VARA Approval Required)
For activities that fall outside VARA’s regulatory perimeter, the DMCC incorporation process is generally efficient. From initial application to licence issuance, founders can typically expect a timeline of 2 to 3 weeks, assuming documentation is complete and there are no structural issues.
Non-Regulated Activities Requiring a VARA NOC
Where a VARA Non-Objection Certificate is required, the process is extended to allow for regulatory review. In practice, founders should budget 4 to 8 weeks, depending on the complexity of the business model and the speed of VARA’s review of the Initial Disclosure Questionnaire.
Regulated VASP Activities (VARA Licence Required)
For fully regulated virtual asset activities, licensing is a two-stage process.
- Stage 1 (DMCC incorporation and Approval to Incorporate): approximately 2-3 months.
- Stage 2 (VARA regulatory review and final approval): typically 6 months or more.
- Stage 1 (DMCC incorporation and Approval to Incorporate): approximately 2-3 months.
The total timeline for regulated crypto businesses can therefore exceed 7 to 9 months, particularly for exchanges, broker-dealers, or custody providers.
What Causes Delays in Practice
Delays most commonly arise from incomplete Initial Disclosure Questionnaires, misaligned business activities, or insufficient compliance frameworks at an early stage. Engaging with DMCC and legal advisors early in the process can materially reduce approval timelines and avoid unnecessary regulatory back-and-forth.
How Much Does It Cost to Set Up a Crypto Company in DMCC?
The cost of setting up a crypto company in DMCC depends on your chosen business activity, company setup options, office solution, and operational requirements. Founders should budget not only for incorporation, but also for the practical costs of launching and operating successfully inside the DMCC free zone.
As a practical benchmark, DMCC company licensing + office package + Founder visas can reach approximately USD 14,000–18,000, depending on the office solution and visa package selected.
|
DMCC Licensing and Incorporation Costs |
DMCC setup costs typically include the application and registration fees, licence issuance fees, and annual licence renewal fees. The exact amount depends on the selected business activity and the company’s structure (e.g., new company vs branch). |
|
Office Space Costs in DMCC |
DMCC requires a physical presence within the free zone. Costs vary depending on whether you choose a flexible desk, co-working space, serviced office, or a larger dedicated office. Office selection also affects the number of visas your company can obtain. |
|
Visas and Immigration Costs |
Most DMCC setups include visa-related expenses such as entry permits, status change (if applicable), medical testing, Emirates ID, and visa stamping. Costs increase based on the number of partners, employees, and dependants sponsored through the company. |
|
Bank Account Setup and Operational Launch Costs |
Launching operations commonly requires additional spend on business planning materials, corporate documentation, internal policies and procedures, and onboarding workflows required by banks and counterparties. Crypto-related businesses should budget for more extensive documentation and longer onboarding processes compared to ordinary trading or consulting companies. |
|
Ongoing Annual Costs to Maintain a DMCC Company |
In addition to yearly licence renewal, DMCC companies should plan for recurring operational expenses such as office lease renewals, visa renewals, accounting, and corporate filings. These recurring costs are often higher than founders expect, particularly for companies scaling headcount and expanding office space. |
Top 3 Mistakes Crypto Founders Make When Setting Up in DMCC
While DMCC offers one of the most structured and supportive environments for launching a crypto business in the UAE, many founders still encounter avoidable delays, regulatory friction, or compliance issues. In most cases, these problems arise not from the framework itself, but from early strategic missteps made during incorporation.
Understanding these common pitfalls can significantly reduce time to market and long-term regulatory risk.
- Assuming a DMCC Trade Licence Equals Regulatory Approval
Many founders incorrectly believe that a DMCC trade licence allows them to conduct all crypto-related activities. In reality, a DMCC trade licence only confirms legal incorporation and permitted business activities. Any activity falling within VARA’s regulatory perimeter requires separate regulatory approval, and operating without it can expose founders to enforcement action and personal liability.
- Misclassifying the Business Activity at Incorporation
Selecting an activity that does not accurately reflect the actual business model is one of the most common and costly errors. Misclassification can delay approvals, trigger regulatory scrutiny, or require restructuring after incorporation. Business activities must be defined with precision and aligned with how the company will generate revenue and interact with virtual assets.
- Underestimating Banking and Compliance Requirements
Founders often focus on incorporation timelines while overlooking the practical requirements for banking, AML/KYC frameworks, and compliance staffing. UAE banks apply enhanced due diligence to crypto businesses, and inadequate preparation can lead to prolonged account opening delays or rejection, even after licensing is complete.
Beyond Licensing: Operating Successfully in the UAE
Once your DMCC crypto licence is issued, your responsibilities as a business operator are just beginning. From regulatory reporting to AML/KYC program oversight, UAE authorities place high importance on ongoing compliance. Key post-licensing areas include:
- Compliance Monitoring: Maintain active supervision systems aligned with VARA expectations (where applicable) and DMCC audit readiness.
- Corporate Governance: Ensure that board and shareholder resolutions remain up to date, especially for businesses with token issuance, custody, or cross-border activity.
- Cross-Jurisdictional Planning: If your business touches other regulatory environments, you may need to harmonize policies to avoid enforcement risk or reputational exposure.
Operating in Dubai provides powerful access to capital, customers, and credibility. However, the bar for legal and operational standards is high. Staying proactive in governance and regulatory affairs is key to long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is a DMCC crypto trade license and who needs it?
A DMCC crypto trade license allows businesses to legally operate crypto-related activities within the DMCC free zone in Dubai. It is required for companies engaging in blockchain development, crypto trading, crypto exchanges or other crypto activities. Depending on the activity, approval may also be needed from the Virtual Assets Regulatory Authority (VARA). DMCC provides a streamlined pathway to obtain this license with structured support at every stage.
2. What are the different types of crypto activities allowed in DMCC?
DMCC allows three main categories of crypto-related activities: (1) non-regulated activities which do not require approval, (2) non-regulated activities requiring a VARA Non-Objection Certificate (NOC), and (3) fully regulated activities requiring a VARA licence. Common activities include blockchain development, consulting, proprietary trading, and running crypto exchanges. Your business model determines which route you’ll follow, and proper classification is key to avoiding delays or compliance risks.
3. Can I start a crypto company in DMCC without living in Dubai?
Yes, you can start a crypto company in DMCC without being a UAE resident. The initial application can be completed remotely, including identity verification and document submission. However, you may need to visit the UAE for visa, banking, or Emirates ID procedures. DMCC supports international founders with flexible setup options and relocation pathways if needed.
4. What are the costs involved in setting up a crypto business in DMCC?
The cost of setting up a crypto business in DMCC varies based on your business activity, office space, and regulatory requirements. For regulated entities, expect to pay DMCC licensing fees plus VARA application and supervision fees, which are tiered based on activity. Additional costs include office lease, visa processing, and bank account setup. It is critical to budget for ongoing compliance and operational expenses.
5. What’s the difference between DMCC and other UAE free zones for crypto?
DMCC stands out for its dedicated Crypto Centre, active support for Web3 companies, and close alignment with VARA. Unlike some other free zones, DMCC offers clearer crypto activity classification, faster onboarding, and better integration with compliance and banking networks. It’s especially attractive for scaling crypto platforms looking for a long-term and credible jurisdiction in the UAE.
6. Can I Start a Non-Regulated Crypto Business in DMCC and Upgrade Later?
Yes, it is possible to start a crypto business in DMCC under a non-regulated activity and later transition to a regulated VARA VASP model, provided the initial activity genuinely falls outside VARA’s regulatory perimeter. The business must operate strictly within the scope of its licensed activity and not conduct any regulated virtual asset services during this period.
Many thanks for Belal Jassoma, Senior Director of Tech Ecosystems at DMCC, and Zaher El Orm, Crypto Centre Manager at DMCC, for contributing to this article. This article was first published in the Founder’s Guide to UAE Crypto Laws (2025 Edition).
Ready to launch in DMCC?
NeosLegal team will set up your DMCC crypto company correctly. We confirm whether you need a VARA NOC or VASP licence, map your regulator and licence path, outline timelines and costs, and deliver a clear execution plan.
About the Author
Irina Heaver is the UAE Crypto Lawyer and Founder of NeosLegal. She has structured over 300 crypto and Web3 projects and advised governments and regulators on crypto asset frameworks.
Legal Disclaimer: This article provides general information about crypto regulation and government liaison strategies. It is not legal advice and should not be relied upon as such. Regulatory requirements vary by jurisdiction and specific business circumstances. Always consult qualified legal counsel in your target jurisdiction before making market entry or compliance decisions.



